The result is a system for digital interactions that does not need a trusted third party. The work of securing digital relationships is implicit — supplied by the elegant, simple, yet robust network architecture of blockchain technology itself.
Defining digital trust
Trust is a risk judgement between different parties, and in the digital world, determining trust often boils down to proving identity (authentication) and proving permissions (authorization).
Put more simply, we want to know, ‘Are you who you say you are?’ and ‘Should you be able to do what you are trying to do?’
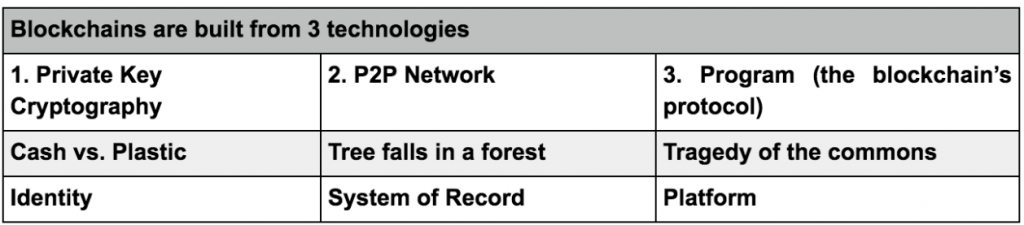
In the case of blockchain technology, private key cryptography provides a powerful ownership tool that fulfills authentication requirements. Possession of a private key is ownership. It also spares a person from having to share more personal information than they would need to for an exchange, leaving them exposed to hackers.
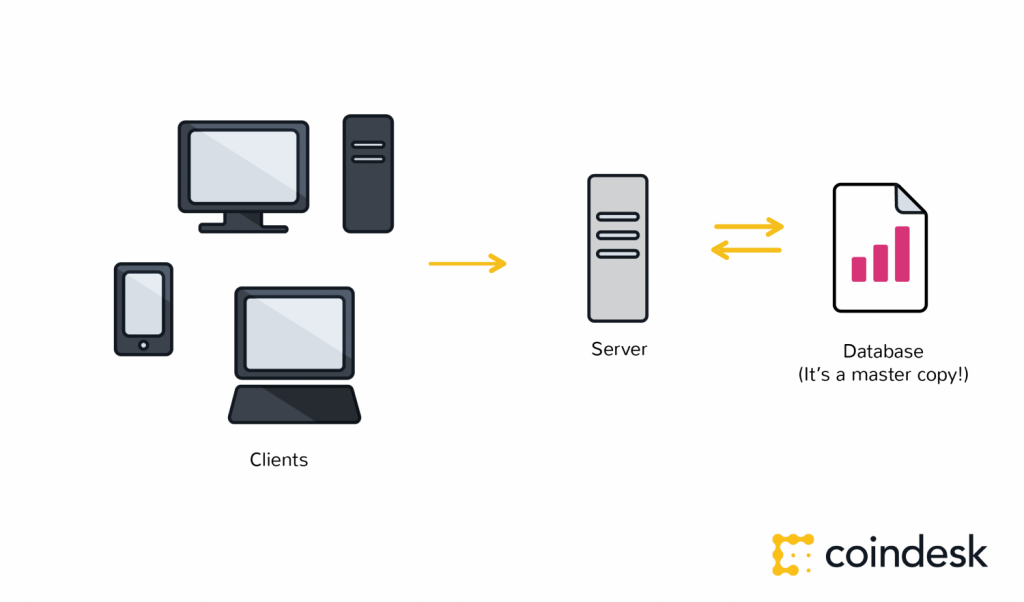
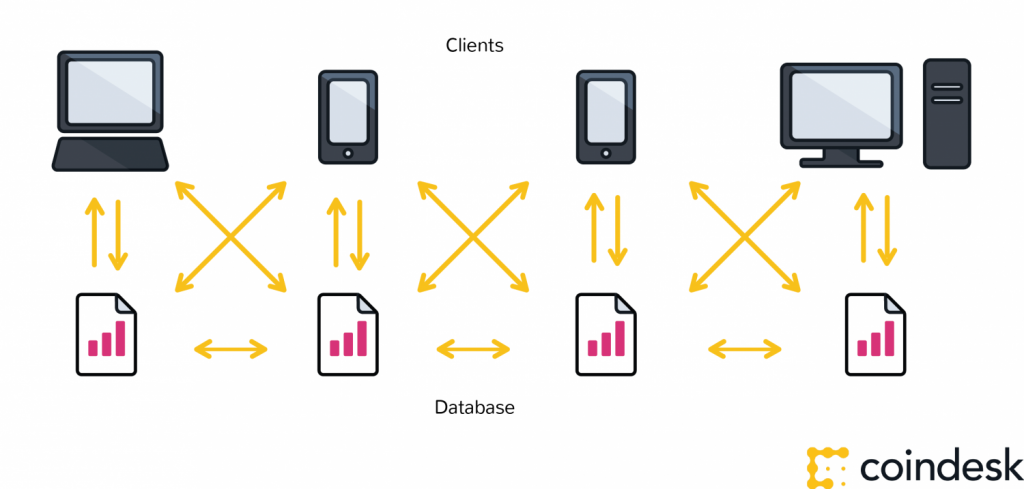
Authentication is not enough. Authorization – having enough money, broadcasting the correct transaction type, etc – needs a distributed, peer-to-peer network as a starting point. A distributed network reduces the risk of centralized corruption or failure.
This distributed network must also be committed to the transaction network’s recordkeeping and security. Authorizing transactions is a result of the entire network applying the rules upon which it was designed (the blockchain’s protocol).
Authentication and authorization supplied in this way allow for interactions in the digital world without relying on (expensive) trust. Today, entrepreneurs in industries around the world have woken up to the implications of this development – unimagined, new and powerful digital relationshionships are possible. Blockchain technology is often described as the backbone for a transaction layer for the Internet, the foundation of the Internet of Value.
In fact, the idea that cryptographic keys and shared ledgers can incentivize users to secure and formalize digital relationships has imaginations running wild. Everyone from governments to IT firms to banks is seeking to build this transaction layer.
Authentication and authorization, vital to digital transactions, are established as a result of the configuration of blockchain technology.
The idea can be applied to any need for a trustworthy system of record.
Source | coinbase
Authored by Nolan Bauerle; images by Maria Kuznetsov