Microsoft Issues Patches for 96 Vulnerabilities
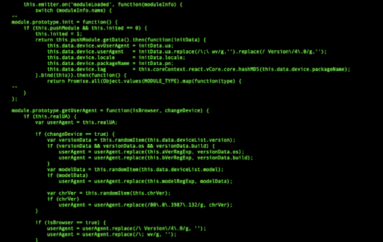
As part of June’s Patch Tuesday, Microsoft has released security patches for a total of 96 security vulnerabilities across its products, including fixes for two vulnerabilities being actively exploited in the wild.
While two of the vulnerabilities have been exploited in live attacks, another three flaws have publicly available proof-of-concept (POC) exploits that anyone could use to target Windows users.
This month’s patch release also includes emergency patches for unsupported versions of Windows platform the company no longer officially supports to fix three Windows hacking exploits leaked by the Shadow Brokers in the April’s data dump of NSA hacking arsenal.
Vulnerabilities Under Active Attack:
The two vulnerabilities currently under active attack include a Windows Search Remote Code Execution flaw (CVE-2017-8543) and an LNK Remote Code Execution bug (CVE-2017-8464).
The more critical of the two is the Windows Search RCE vulnerability which is present in most versions of Windows and resides in the Windows Search Services (WSS) — a feature that allows users to search across multiple Windows services and clients.
The vulnerability, which already has publicly disclosed POC exploit code since early February, could allow a remote code execution in the Windows operating system, enabling an attacker to take over the target machine remotely via a network connection.
The SMB vulnerabilities can be extremely dangerous, and the best example of it is the WannaCry ransomware that exploited an SMB flaw within a network to replicate itself to all unpatched machines very quickly.
Windows Server 2016, 2012, 2008 along with desktop systems such as Windows 10, 7 and 8.1 are all affected by this vulnerability.
Another critical flaw under active exploitation is LNK RCE vulnerability resides in the way Windows handles LNK desktop shortcuts, which could allow remote code execution if the icon of a specially crafted shortcut is displayed to a user.
Besides this, the Edge browser also receives patches for three more flaws (CVE-2017-8496, CVE-2017-8497, and CVE-2017-8499) that would enable attackers to carry out remote code execution on vulnerable users.
Other patches include fixes for nine of its own remote code execution flaws in Office that could be targeted via DLL files, email messages, a website, and a PowerPoint file.
Source | thehackernews